John Cage
1912–1992
Introduction
John Milton Cage Jr. (September 5, 1912 – August 12, 1992) was an American composer and music theorist. A pioneer of indeterminacy in music, electroacoustic music, and non-standard use of musical instruments, Cage was one of the leading figures of the post-war avant-garde. Critics have lauded him as one of the most influential composers of the 20th century. He was also instrumental in the development of modern dance, mostly through his association with choreographer Merce Cunningham, who was also Cage's romantic partner for most of their lives.
Cage's teachers included Henry Cowell (1933) and Arnold Schoenberg (1933–35), both known for their radical innovations in music, but Cage's major influences lay in various East and South Asian cultures. Through his studies of Indian philosophy and Zen Buddhism in the late 1940s, Cage came to the idea of aleatoric or chance-controlled music, which he started composing in 1951. The I Ching, an ancient Chinese classic text and decision-making tool, became Cage's standard composition tool for the rest of his life. In a 1957 lecture, "Experimental Music", he described music as "a purposeless play" which is "an affirmation of life – not an attempt to bring order out of chaos nor to suggest improvements in creation, but simply a way of waking up to the very life we're living".
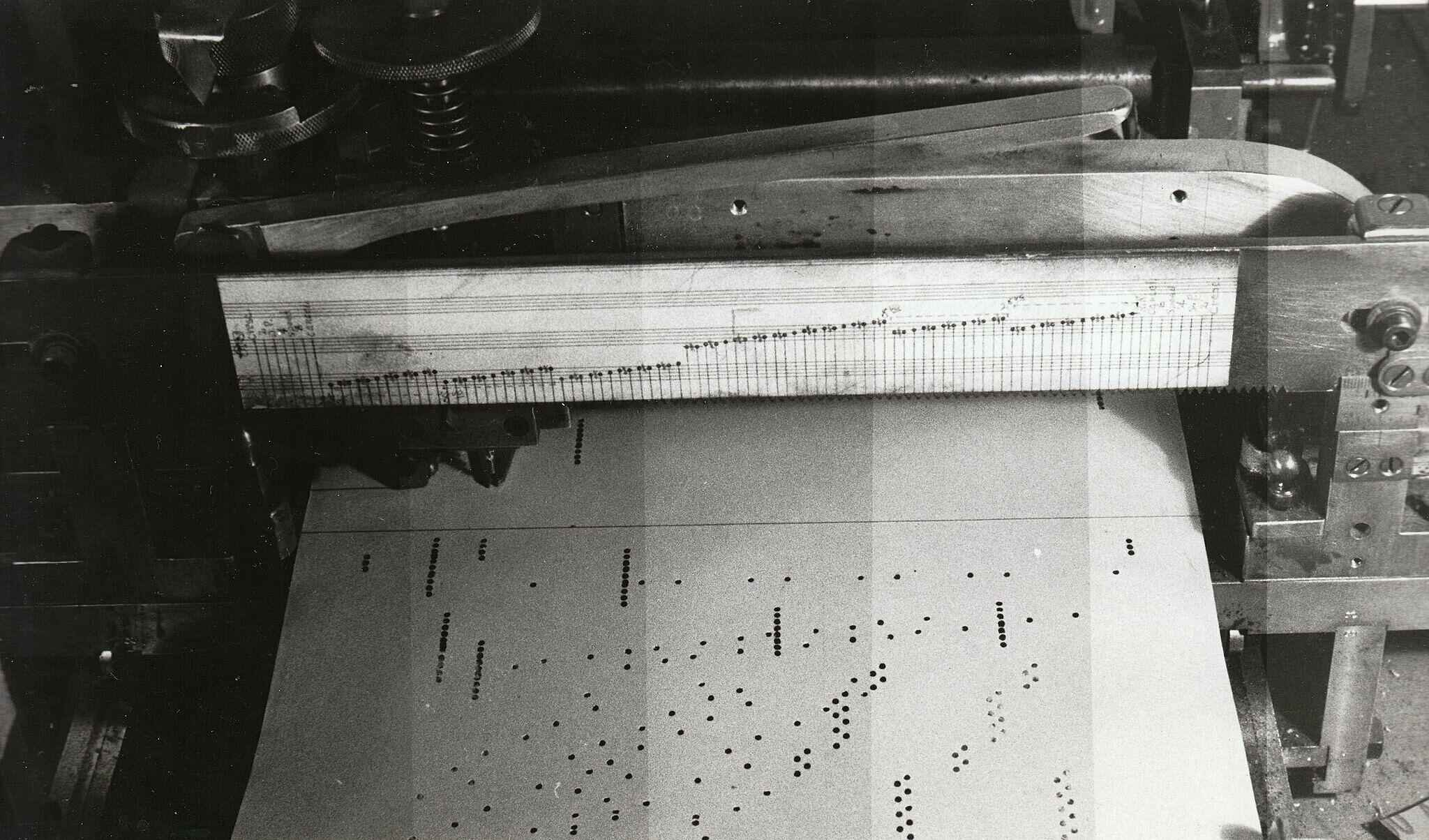
Cage's best known work is the 1952 composition 4′33″, a piece performed in the absence of deliberate sound; musicians who perform the work do nothing but be present for the duration specified by the title. The content of the composition is intended to be the sounds of the environment heard by the audience during performance. The work's challenge to assumed definitions about musicianship and musical experience made it a popular and controversial topic both in musicology and the broader aesthetics of art and performance. Cage was also a pioneer of the prepared piano (a piano with its sound altered by objects placed between or on its strings or hammers), for which he wrote numerous dance-related works and a few concert pieces. These include Sonatas and Interludes (1946–48).
Wikidata identifier
Q180727
Information from Wikipedia, made available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License . Accessed February 16, 2026.
Introduction
Originally trained as an abstract painter, Cage abandoned the medium in favor of composition, which he studied with Henry Cowell and Arnold Schoenberg. In the 1940s, becoming interested in expanding the range of percussive instruments, he developed the "prepared piano", composing works for a piano with various objects placed between the strings. After studying Zen Buddhism, Cage began to work toward a new theory of composition, focusing on removing intention and personal taste, with attention paid to the process and the element of chance. Regarding silence on equal terms as structured sound and noise, in 1952 Cage produced 4'33", a composition in which no sound is made. Cage was a strong influence and a collaborator with many visual artists, and including his life partner the dancer and choreographer Merce Cunningham.
Country of birth
United States
Roles
Artist, author, composer, graphic artist, lecturer, painter, philosopher, sculptor, theorist, writer
ULAN identifier
500092036
Names
John Cage, J. C., Jr. John Milton Cage, Dzhon Keĭdzh, Jon Kēji
Information from the Getty Research Institute's Union List of Artist Names ® (ULAN), made available under the ODC Attribution License. Accessed February 16, 2026.